Projects
of the European Project Center
Ongoing projects

New european bauhaus for increasing urban biodiversity
| Project Budget (total) | 1.631.680,00 Euro |
| Project Budget (Wismar) | 162.250,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 01.06.2024 - 30.11.2026 |
| Lead Partner | Wrocław University of Environmental and Life Sciences |
| Project Partner | City of Kranj (Slovenia), Institute for Sustainable Development (Slovenia), City of Pula (Croatia), POR Consult, Projects of Sustainable Development (Croatia), BURST Nonprofit Llc (Hungary), Research and consultancy centre of Milan's Polytechnic UNI on environmental and territorial planning (Italy), Hochschule Wismar: Technology, Business and Design (Germany), Municipality of Wroclaw (Poland), Erd County City (Hungary) |
The loss of biodiversity due to climate change is enormous, also in urban areas. To counter this negative development, the URBIO BAUHAUS project protects and boosts urban biodiversity by combining aesthetic design, citizen participation, and science. With this holistic approach, the project innovatively integrates “New European Bauhaus” principles to develop urban biodiversity solutions. The partners create and test biodiverse islands to preserve keystone species together with affected citizens and deliver a transnational policy master plan for further fostering long-term collaborations between science, policy makers, and locals.

Hub for AI and IT knowledge and cooperation between universities and SMEs
| Project Budget (total) | 199.962,00 Euro |
| Project Budget (Wismar) | 46.998,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 01.09.2024 - 28.02.2026 |
| Lead Partner | Klaipeda University (Lithuania) |
| Project Partner | Blekinge Institut of Technology (Sweden), West Pomeranian University of Technology in Stettin (Poland), Hochschule Wismar (Germany) |
AIKnowIT involves four partners from Lithuania, Sweden, Poland and Germany. The partnership is composed of universities and technology institute. The partners are supported by 1 associatedpartner which is science and technology park. The project is led by Klaipeda University (LT). The overall project objective is to build platform for cooperation between universities and SMEs to enableexchange of knowledge and strengthen the connectivity by empowering digital innovation by application ofartificial intelligence and cybersecurity solutions.The project’s activities will start with workshops and surveys to collect the needs and demands frominterested parties to be addressed by the platform. Analysis of the survey will be used to shape the platformin a suitable form.The main target groups are entrepreneurs, startups and other business professionals, economicdevelopment organizations, students, and interns.

Democracy festivals for the youth
| Project Budget (total) | 2.288.981,10 Euro |
| Project Budget (Wismar) | 199.850,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 01.07.2024 - 30.06.2027 |
| Lead Partner | Association of Polish Communes Euroregion Baltic |
| Project Partners | Center of European Meetings "Światowid" in Elbląg (Poland), Media Design Association (Poland), Olsztynek Commune (Poland), Cultural administration, Hässleholm Municipality (Sweden), Municipality of Västervik (Sweden), Hochschule Wismar (Germany), Förderverein Guthaus Ramin (Germany), Klaipeda University (Lithuania), Association Rietavas Women Employment Centre (Lithuania), Guldborgsund Municipality (Denmark), Odsherred Municipality (Denmark) |
The D-effect project promotes the cooperation of youth-oriented stakeholders in the South Baltic Area and contributes to building the problem-solving capabilities of stakeholders from Sweden, Danmark, Germany, Poland and Lithuania. Thus, it adds a new element to capabilities of better youth participation, engagement, and increased education of democratic values that can make local societies more sustainable and resilient and the entire region a more youth-friendly place.
Local engagement and activism strategies for selected model regions that combine measures for civic participation, democratic and EU values engagement and promoting multisectoral stakeholder & youth acceptance, understanding, and long-lasting cooperation will be developed. As well as a set of complementary pilot measures for democratic engagement and dialogue that depict typical use cases, and that adapt, test, and validate concrete solutions for the transferability of experiences in the South Baltic Area which will enable of participation of a wide range of stakeholders.
The results are processed into a “D-Effect Toolbox” which will be promoted and disseminated by the newly established “SB Youth-oriented Helpdesk”, which will serve local communities with experience and support. It gives other local authorities, and youth specialists concrete guidance on how to foster youth policies/actions and is pro-actively and widely disseminated to them. The project will put into practice the local perspective of new methods and tools of democracy promotion based on democracy festivals as open platforms that unite different actors, groups, experiences, and dimensions. Based on the assumption that democracy is more than democratic institutions and written rules, but a culture to be nurtured by creating spaces and platforms where people can physically meet, talk to each other, get inspired, exchange opinions, and debate their ideas.
D-effect turned towards networking activities at the local level. In this regard, steered towards the practical dimension of building engagement with different communities, and foster active civic engagement, a culture of discussion, and critical thinking in response to the alarming rise of authoritarianism and nationalism.

Better paper packaging management
| Project Budget (total) | 1.452.835,00 Euro |
| Project Budget (Wismar) | 244.000,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 01.07.2024 - 31.06.2027 |
| Lead Partner | Gdańsk University of Technology |
| Project Partners | Gdańsk Entrepreneurship Foundation (Poland), enviMV e. V. environmental technologies from Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (Germany), Klaipėda science and technology park (Lithuania), City disposal Rostock LLC (Germany), CLEAN - Environmental Cluster (Denmark) |
The BePacMan project aims to extend the life cycle of paper packaging. This is both commercially and ecologically attractive for small and medium-sized companies in particular.
Within the project, the current situation is first analysed and evaluated in order to then develop practical solutions. The aim is to develop new concepts that improve the situation of trade and industry. The main target group therefore includes small and medium-sized enterprises, NGOs, regional authorities, logistics companies, but also the consumers themselves.

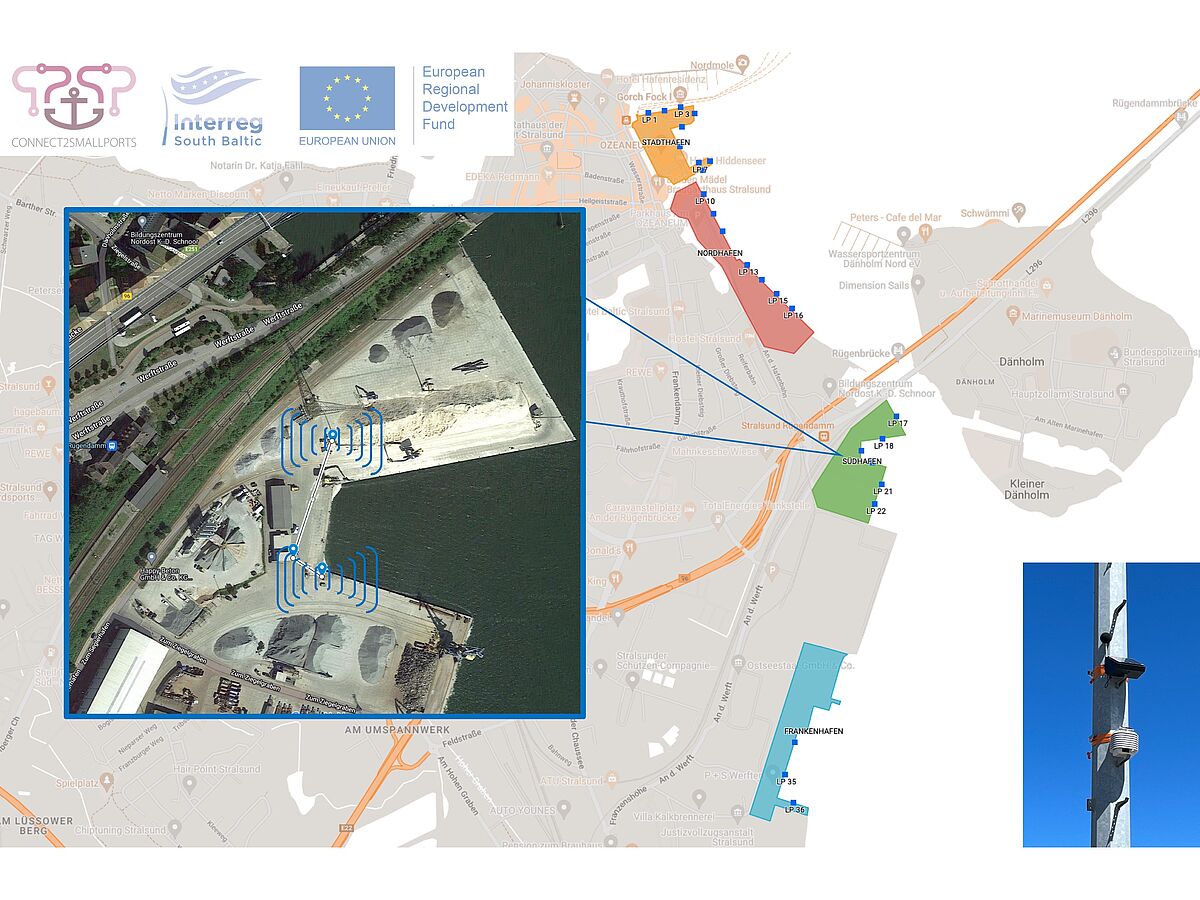
Decarbonisation of Small Ports' Ecosystems for Efficient Environmental and Energy Management towards South Baltic Fit for 55
| Project Budget (total) | 1.680 450,00 Euro |
| Project Budget (Wismar) | 338.250,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 15.09.2023–14.09.2026 |
| Lead Partner | Hochschule Wismar, University of Applied Sciences (Wismar, Germany) |
| Project Partners | Klaipėda Science and Technology Park (Klaipėda, Lithuania); Motus Foundation (Gdynia, Poland); Blekinge Institute of Technology (Karlskrona, Sweden); Maritime University of Szczecin (MUS, Szczecin, Poland); Elbląg Sea Port Authority Ltd. (Elbląg, Poland), Klaipėda State Seaport Authority (Klaipėda, Litauen), Euro-Terminal Świnoujście (Świnoujście, Polen) |
In the Southern Baltic Area (SBA), most ports are classified as Small and Medium Sized Ports (SMSPs), which have greater barriers to start green transition compared to large ports due to lower financial capacity, lack of human resources and lower policy support. Nevertheless, they are equally affected by European environmental targets and legislation. Therefore, it is necessary to support SMSPs in their green transition and decarbonisation. For this reason, the project aims at providing access to missing knowledge on green transition and decarbonisation for such ports by developing and deploying two solutions by the end of 2026:
- Green Energy Harmonisation Toolbox for SMSPs
- EU Regulation and Green Policy Compliance Roadmap of Green Transition for SMSPs

Innovation Hubs for Tech, Art and Business
| Project Budget (total) | 1.988.002,65 Euro |
| Project Budget (Wismar) | 256.530,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 01.09.2023-31.08.2026 |
| Lead Partner | Blue Science Park (Sweden) |
| Project Partners | Karlskrona Municipality (SWE); Hyper Island Programme AB (SWE); West Pomeranian IT Cluster (POL); Rietavas Tourism and Business Information Centre (LTU); Academy of Arts Szczecin (POL); Media Dizajn (POL); Talent Garden Rainmaking (DNK); Hochschule Wismar, University of Applied Sciences (GER) |
The aim of the project is to increase expertise, knowledge transfer and cooperation with businesses through the interdisciplinary networking of the fields of technology, art and business.
In particular, the approaches, competences and skills of the Cultural and Creative Industries (CCIs) will be used to develop new value creation paradigms in different sectors. Cooperation is essential to achieve common goals and to enable European regions to effectively address regional and sectoral challenges together.
The aim of the T.A.B. project is to create international, cross-sectoral platforms to establish transnational cooperation links between regional and national economic and cultural sectors. The approaches, competences and skills of the Creative and Cultural Industries (CCIs) are fundamental to the development of new value paradigms in various sectors.
These effects can already be seen in the way businesses communicate. New forms of aesthetics, web presence and storytelling campaigns are important applications that the creative world can contribute to. Last but not least, AI will play an increasing role.

Technology Transfer for thriving Recirculating Aquaculture Systems in the Baltic Sea Region
| Project Budget (Total) | 2.364.442,64 Euro |
| Project Budget (Wismar) | 225.000,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 01.01.2023 - 31.12.2025 |
| Lead Partner | Klaipeda Science and Technology Park (LT) |
| Project Partners | SUBMARINER Network for Blue Growth EEIG (DE); Klaipeda University (LT); Blue Research ApS (DK); Ida-Viru Investment Agency (EE); Gludborgsund Kommune (DK); University of Gdansk (PL); Business Lolland-Falster (DK); Hochschule Wismar, University of Applied Sciences (DE); AB Linas Agro Group (LT) |
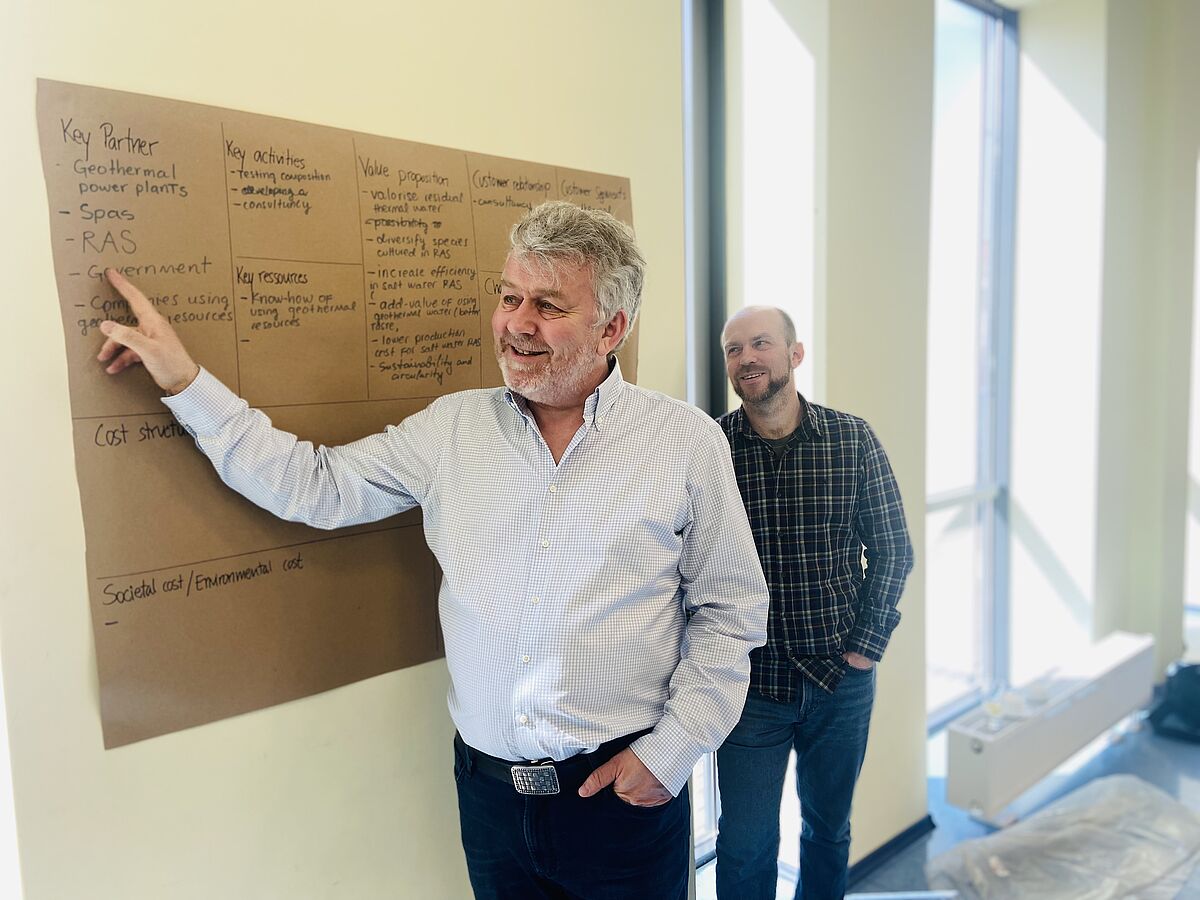
The TETRAS project addresses a challenge that affects all regions of the Baltic Sea Region: how to reconcile economic development with social and environmental goals. Much of the excess water or energy used in industry is lost to the environment. What if we could capture these resources and use them for food production? How can we use water intelligently to balance the needs of industry with the most modern food production systems? The solution is called RAS: Recirculating Aquaculture Systems. On their own, RAS are expensive and energy-intensive. However, as an industrial "add-on", RAS can be highly efficient methods of food production. For example, in combination with geothermal heat exchange, water reuse (e.g. so-called "engineered" water) or agro-aqua symbioses such as aquaponics. Besides food, RAS creates additional revenue streams, e.g. by-products for use in cosmetics, bioplastics, fertilisers or biogas. TETRAS will demonstrate how RAS can be placed in strategic geographical locations or combined with industrial processes to increase efficiency while producing affordable, healthy food. The partnership will jointly develop regional pilots and standardised tools for municipalities to assess and monitor RAS applications and align them with appropriate sectors. These tools will enable authorities to integrate RAS into regional development strategies, contributing to both sustainable waters and the transition to a circular economy in a win-win scenario.
The TETRAS partnership consists of ten partners from five Baltic Sea countries: Denmark, Lithuania, Poland, Germany and Estonia. The project is supported by a large number of associated organisations, including organisations from Sweden and Finland.

Strengthening the cultural and creative industries as drivers of socio-ecological transformation in rural areas
| Project Budget | 434.349,86 Euro |
| Project Duration | 01.03.2023 - 28.02.2026 |
| Lead Partner | Hochschule Wismar, University of Applied Sciences: European Project Center |
| Project Partners | Hochschule Magdeburg-Stendal |
The project "LandStarK" sees itself as the establishment of a methodical and practical lighthouse for the facilitation and revitalisation of cultural and creative activities as well as participation in rural areas (regions) in Germany as part of the systemic change and the increasing departure towards sustainable transformation. Building on scientific and transfer excellence, this lighthouse will open up new ways of thinking and acting in socio-economic ecosystems in the eight participating rural areas in four above-mentioned federal states from March 2023 to February 2026.
The integration of eight rural regions under one roof in the four-country corner builds on both existing and new cooperations and promises better coherence. All participating regions are connected via common borders, which favours the formation of a common cluster and reduces subsequent dispersion losses.
The research focuses on an interdisciplinary and interregional cooperation of the eight rural areas - counties on the federal level and NUTS3 regions on the EU level, which have a common denominator due to their circumstances, such as low settlement density and number of inhabitants, a high proportion of agricultural and forestry land, loose residential development and peripheral location to large centres such as Berlin and Hamburg.
The focus of the project is to capture patterns of cooperation, interactions and mechanisms of action of the cultural & creative industries (CCIs) using the example of rethinking and transformation processes in two given economic ecosystems - organic farming and tourism. Ecosystems can be considered as markets that include operational, ecological, economic, technological and legal dimensions. Among these are the submarkets of the food industry, gastronomy and mobility. These were selected because there have been hardly any studies on the topic of intersectoral cooperation between the NPP and these sectors in the context of the system change that has begun. Furthermore, tourism is an important economic backbone in all participating regions to increase the added value of a structurally weak region. Organic farming and sustainable use, provision of agricultural products, services and their linkage with NPP as well as the resulting macroeconomic and social innovation effects have also hardly been explored so far and play an increasing role with regard to climate change.
Accordingly, four specific following questions are raised in this research project:
(1) How and to what extent can the NPP trigger rethinking and transformation processes in the sense of the Great Transformation (social, ecological, inclusive) in rural areas using the example of rural sectoral specialisation (tourism and organic farming) and thus pave the way for sustainable resilience of the participating rural areas?
(2) How can positive secondary and tertiary effects of NPP on specific order-economic ecosystems and their interactions with NPP in rural areas be quantified and qualified?
(3) Which cultural and creative endogenous resources, formats, methods (e.g. organisational culture, social / cognitive / institutional proximity and density, market forces, regulatory framework) set rethinking and transformation in motion and are crucial for sustainable system change?
(4) To what extent can studied intersectoral cooperation with NPP be adopted in other economic ecosystems outside organic farming and tourism?

Advancing circular economy in partner countries by development and implementation of Master programme "Waste Management"
| Project Budget | 864.624,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 15.01.2021 - 14.01.2025 |
| Lead Partner | Hochschule Wismar, University of Applied Sciences: European Project Center |
| Project Partners | Tallinn University of Technology (EE); Ekonomikas un Kulturas Augstskola (LV); A. Baitursynov Kostanay State University (KZ); Sh.Ualikhanov Kokshetau University (KZ); S. Seifullin Jazakh Agrotechnical University Nur-Sultan (KZ) |
Due to the attack on Ukraine, the European Union has decided that no more Russian partners may be involved in the projects. Therefore, the project is currently only being implemented with partners from Estonia, Latvia and Kazakhstan.
EU Environment Action Programme was initiated, addressing the long-term EU strategy on waste, based on the 2005 Thematic Strategy on the Prevention and Recycling of Waste and the subsequent Waste Framework Directive.
Although these action plans and strategies have undoubtedly had a significant impact on environmental awareness and efficient waste management, further action should be taken with the support of neighbouring countries, especially those producing a similar amount of waste (i.e. 6 tonnes of waste per 16 tonnes of annual personal consumption).
Both the Russian Federation and Kazakhstan are countries which, on the one hand, have a huge territory (1st and 9th largest country in the world, respectively) and, on the other hand, in Soviet times had relatively low household waste generation (due to much lower household consumption). As a result, the main way of waste disposal in both countries was (and still is) landfill; however, the situation has changed drastically in the last decade and today the amount of waste per person in these countries is close to the EU level.
The overall objective of the project is to influence the current situation by (1) developing engineering-based waste management curricula at master's level and (2) raising awareness of circular economy by developing new curricula in higher education institutions. This project would enhance practice-based learning to ensure parallel development of soft skills (teamwork, communication, management, decision making) and hard skills (waste management) and provide evidence of problem solving to future employers. Main target group: engineering students. Indirect beneficiaries of the project are: Industry partners, non-profit organisations and policy makers.
Expired projects
2023

Accelerating ICT students' startup development competence via interdisciplinary modular courses in the HEI curricula
| Project Budget | 815.609 Euro |
| Project Duration | 15.11.2019 - 14.11.2023 |
| Lead Partner | Hochschule Wismar, University of Applied Sciences: European Project Center |
| Project Partners | Tallinn University of Technology (EE); EKA University (LV); Kostanay State University (KZ); Almaty Management University (KZ); Caspian State University (KZ) |
Due to the attack on Ukraine, the European Union has decided that no more Russian partners may be involved in the projects. Therefore, the project is currently only being implemented with partners from Estonia, Latvia and Kazakhstan.
In today's labour market, there is a high demand for ICT skills in all areas of engineering and technology professions, and this demand is even greater in the entrepreneurial sector, as IT business is one of the fastest growing areas. Currently, neither ICT nor engineering or technology students receive entrepreneurship training at partner country universities (their business curricula are usually limited to basic economic theory and the organisation of production units). Engineering and technology courses also rarely receive sufficient training in ICT, especially in emerging IT technologies - partner country universities teach ICT skills in the form of some software engineering tools without providing opportunities for lifelong learning in this area.
Project goals:
1) Improve Kazakh and Russian engineering curricula at partner universities by introducing an ICT skills-based entrepreneurship module.
2) Introduce an IT-entrepreneurial acceleration programme for soft skills development in engineering curricula by bringing together the strengths of partner universities in terms of collaborative teaching, assessment and feedback.
3) Alignment of engineering education with EU standards in accordance with the Bologna Process through the introduction of common university courses recognised by the consortium of partner universities.
4) Promote the approach of international bottom-up collaboration within the knowledge triangle so as to improve the level and structure of ICT hard skills and entrepreneurial soft skills acquired by engineering students.

TRAINing on ECOinnovation in electronics product development
| Project Budget | 196.310,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 01.11.2020 - 31.08.2023 |
| Lead Partner | Tartu University (EE) |
| Project Partners | Hochschule Wismar, University of Applied Sciences (DE); Centria University of Applied Sciences (FI); Riga Technical University (LV) |
The main objective of the TRAIN-ECO project is to develop training materials on eco-innovation for electronics professionals and entrepreneurs from SMEs and start-ups. SMEs and start-ups play an important role in the EU economy and need to move towards sustainable business models to support the EU's efforts to build a green economy. For Example, Waste from the electronics industry, known as e-waste, is an increasingly big problem for the EU and the world. Currently, however, SME and start-up employees lack the training and skills
necessary to develop innovative and environmentally sound electronic products that comply with EU regulations. To remedy this, TRAIN-ECO:
- Development of training materials on eco-innovation leading to sustainable development and quality management in the development of electronic products
- Development of training material on EU environmental and safety standards
- Design a MOOC that comprehensively covers the above topics.
- Creation of shorter e-modules on these topics and an open repository of project materials
- Produce guidelines for VET providers on how to integrate our learning materials into flexible continuing education programmes and courses.
All our objectives have been set in recognition of the specific needs of electronics professionals and entrepreneurs. As working professionals often lack the time to participate in longer-term training programmes, TRAIN-ECO will pay special attention to creating flexible learning opportunities for this group, in particular through the development of a MOOC and a series of shorter e-modules on eco-innovation. In addition to SME and start-up employees, we will target learners in further education, students of electrical engineering and vocational education and training, and adult education providers, who will be able to use the TRAIN-ECO materials freely.
2022

South Baltic Small Ports as Gateways towards Integrated Sustainable European Transport System and Blue Growth by Smart Connectivity Solutions
| Project Budget | 2.117.175,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 01.07.2018 - 30.06.2022 |
| Lead Partner | Hochschule Wismar, University of Applied Sciences |
| Project Partners | Klaipeda Science and Technology Park (LT); Motus Foundation (PL); Blekinge Institute of Technology (SE); INWL Institute for Sustainable Economics and Logistics (DE); Seehafen Wismar GmbH (DE); NPPE Klaipeda Shipping Research Centre (LT); Klaipeda State Seaport Authority (LT); Port of Karlskrona – Municipality of Karlskrona (SE) |
According to the forecast of the International Transport Forum (2015), shipping traffic will increase by 327% by 2050, causing 238% more CO2 emissions. In Europe, freight volumes will increase by 216 % by 2050, causing 174 % more CO2 emissions. There will be a huge shift in the transport of goods. This will have a major impact on sea and inland ports. Small and medium-sized ports building the so-called comprehensive TEN-T network are expected to face strong environmental, competitive and operational pressures. 66% of all ports in the BSR are small and medium-sized ports. Total cargo throughput is less than 2 million tonnes per year. Small ports, especially in the SBSR, suffer from lower cargo volumes, lack of smart specialisation, outdated infrastructure, investments and new business models that contribute to blue and green growth. They are unable to secure their funding, which is paradoxical. After all, theoretical and empirical studies in the US and Europe show (Rodrigue and Schulman, 2013, Rozmarynowska and Oldakowski, 2013), port infrastructure projects promote economic development. So far, however, this has only been the case for large ports. These are so-called core ports of the TEN-T network, e.g. Rostock, Szczecin, Gdynia, Klaipeda, Malmö, Trelleborg (SBSR scale). In contrast, the small ports of Wismar, Sassnitz (DE); Fredericia, Ronne, Rodby (DK); Ystad, Karlskrona, Karlshamn (SE) and Police (PL) are also in the SBSR. They are part of the overall TEN-T network and receive financial and economic support. Nevertheless, they face tough survival conditions. Competition is even stronger for small SBSR ports that are not part of the overall TET-T network (e.g. Stralsund, Kolobrzeg, Elblag, Łeba (PL), Kalmar (SE)). Paradoxically, they form hubs of the regional economy and are important gateways for regional development. In Poland alone there are about 38 such small ports. We are in line with the EU White and Green Papers, the CET Facility, Council Regulations and ESPO and BPO recommendations.
2021

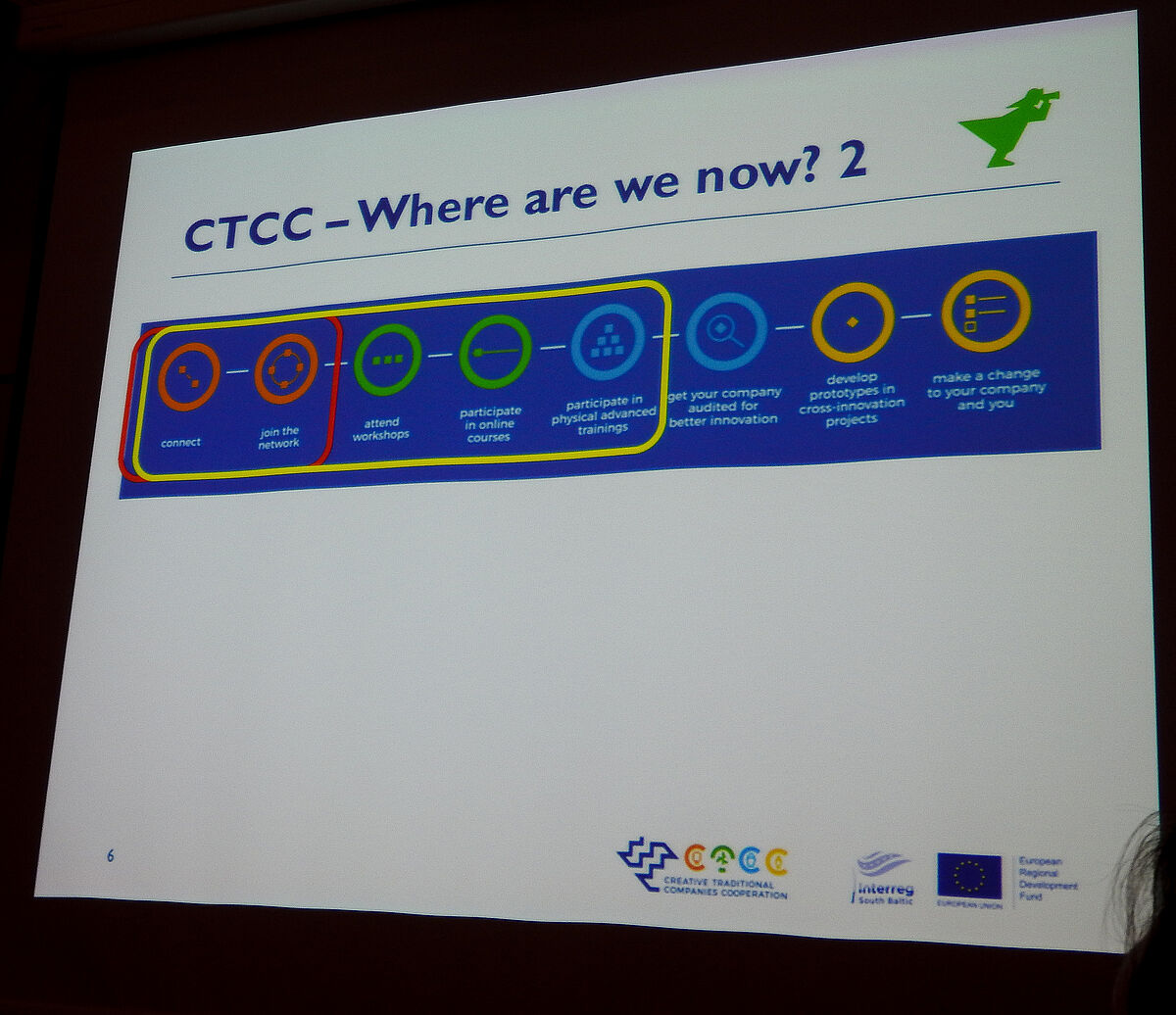
Creative Traditional Companies Cooperation
| Project Budget | 1.583.075,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 15.07.2017 - 30.06.2021 |
| Lead Partner | Hochschule Wismar, University of Applied Sciences: European Project Center |
| Project Partners | ATI erc gGmbH education, research and furtherance of cooperations (DE); Season of Creativity e. V. / FINT e.V. (DE); Public institution Rietavas Tourism and Business Information Centre (LT); Association Rietavas Women Employment Centre (LT); Klaipeda Science and Technology Park (LT); Media Dizjan (PL); Pomeraniam Science and Technology Park (PL); Association of Polish Communes of Euroregion Baltic (PL); Blekinge Institute of Technology (SE) |
Traditional industries are the backbone of the regional economy, but they suffer from the pressure of environmental impacts. Maritime transport is crucial for regional development and for the EU as a whole, as around 90% of goods destined for markets outside the EU are transported by sea. Maritime activities such as transport and shipbuilding, energy production and use, and coastal tourism, including smaller infrastructures (yachts and cruises), are forced by environmental pressures (e.g. to reduce greenhouse gas and other emissions) to seek new innovative and sustainable solutions, to comply with new policy regulations for transport and related activities, and to change negative or ZERO innovation performance, as shown in the recent JRC Technical Report on Blue Growth and Smart Specialisation (2016).
CTCC improves the innovation performance of the main target group - at least 200 Danish, German, Polish, Lithuanian and Swedish small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) from the Southern Baltic Sea Region (SBSR) by 30 June 2020 from three targeted traditional production sectors contributing to blue and green growth. Improving the innovation performance of traditional SMEs will be achieved through cross-sectoral cooperation with 100 freelancers, start-ups and SMEs from three creative industries. The project offers four cross-border solutions for innovation development, management and exploitation: 1) a triple helix partnership between creative industries and businesses and a platform for creative brokerage that facilitates innovation; 2) a cross-sector innovation training methodology; 3) 30 specific demand-driven innovation solutions for traditional SMEs and regions, such as. e.g. environmentally friendly and ergonomic ship design, simulators for maritime applications; improved and safe navigation signs in ports and coastal areas; and 4) four sustainable, self-running and funding mechanisms for the use of the developed models beyond the project lifetime.

Internationalization of South Baltic maritime economy
| Project Budget | 1.927.125,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 01.07.2017 - 30.06.2021 |
| Lead Partner | Gdansk International Fair Co (PL) |
| Project Partners | TNOiK - Scientific Society for Organization and Management (PL); Rostock Business and Technology Development (DE); Hochschule Wismar (DE); Public Institution Strategic Self-Management Institute (LT); Chamber of Commerce, Industry and Crafts (LT) |
The maritime industry is one of the most promising development sectors in the SB region, but despite strong lobbying and support from SB regional authorities for the intensive development of the maritime industry, there is still a lack of international instruments across the SB region to support SME marketing activities at the international level.
The INTERMARE project will support the maritime economy across the Southern Baltic region through a network of businesses and stakeholders under a common INTERMARE brand that is easily recognisable in the region and in other European and global markets.
The aim of the project is to create a network of companies and stakeholders (clusters, employers' organisations, regional and local authorities, etc.) for greater recognition of SMEs from the SB region in international markets and better cooperation in supply chains in the region. The INTERMARE project will develop and implement a series of measures to integrate stakeholders in the SB region. This will allow for better cooperation and the creation of joint projects and initiatives, enabling maritime SMEs from the region to compete in the markets.
The maritime companies of the region will be able to promote themselves at international events within the framework of the common regional network (brand) of the INTERMARE SB region, e.g. maritime fairs, cross-border network meetings and promotional activities in Europe. To this end, the following results are to be achieved:
Marketing strategy for the maritime economy in the Southern Baltic Sea Region;
Creating tools to support and facilitate international cooperation and promotion of blue economy businesses in the Southern Baltic Sea Region;
Creation and use of tools to promote the blue economy through actions and events;
INTERMARE 2020, a trade fair for blue economy businesses.
The project involves six partners from Poland, Lithuania and Germany, but is also open to SMEs from Denmark and Sweden.

LABORATORY NETWORK FOR TESTING, CHARACTERISATION AND CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT OF ELECTRONIC PRODUCTS DEVELOPED BY SMES
| Project Budget | 1.780.000 Euro |
| Project Duration | 01.10.2017 - 30.09.2020 |
| Lead Partner | University of Tartu (EE) |
| Project Partners | Riga Technical University (LV); University of Latvia (LV); Ventspils University College (LV); Applied Research Institute for Prospective Technologies (LT); Centria University (FI); Hochschule Wismar (DE); JSC Modern E-Technologies (LT); SIA "JLU Technologies" (LV); Crystalspace (EE); LTD VIZULO (LV); LCC "Cryogenic and Vacuum Systems" (LV) |
TEST-4-SME initiates an innovation support network in the Baltic Sea Region that provides testing and consultancy for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the electronics sector during early product development. The tests and consultations focus on how to demonstrate conformity with international standards. All electronic products must demonstrate their conformity with standards, which requires testing of product prototypes. Early testing can help avoid errors at later stages and thus save costs.
Members of the network advise and train company staff on standards compliance and share knowledge within the network to improve the quality and efficiency of testing, speeding up the electronics companies' product development process.
As part of the project, seven companies are testing the services of the network. The project will establish a list of electronics testing laboratories, develop rules for the network and analyse the demand for existing testing services in the region. The network is open for more electronics testing labs. Some investments in testing equipment are planned. The laboratory staff will be trained. The testing services will be evaluated and the long-term sustainability strategy planned.
2020

Regional Observatories for supporting the Development of Smart Specialization
| Project Budget | 2.560.000 Euro |
| Project Duration | 10.06.2017 - 31.05.2020 |
| Lead Partner | Upper Silesian Agency for Entrepreneurship and Development Ltd. (PL) |
| Project Partners | Lubelskie Voivodeship (PL); FH JOANNEUM GmbH - University for applied sciences (AT); The University of West Bohemia (CZ); Regional Innovation Agency of South Great Plain Association of Public Utility (HU); INNOVA Észak-Alföld - Regional Development and Innovation Agency Nonprofit Ltd. (HU); Research and Development Center of Electric Machines (SI); Jasa Association (SI); Hochschule Wismar - University of Applied Sciences: Technology, Business and Design (DE); ATI erc gGmbH education, research and furtherance of cooperations (DE); Confindustria Veneto SIAV S.p.A (IT); Langhe Monferrato and Roero Development Agency (OT) |
In Central Europe, regional innovation strategies (RIS) and the actual end-user needs for smart specialisation are too often not well aligned. As each region collects relevant data in different structures, the SMART_watch project will develop a common methodology and benchmarking tools to improve the situation. Specifically, the project will develop a model for regional sector observatories equipped with a set of monitoring and benchmarking tools available to all RIS stakeholders and smart market actors.
As the project coincides with the mid-term evaluation of RIS, the partners will develop policy recommendations for EU institutions based on international pilot projects and research results. A newly created network of regional sector observatories will enable national and EU authorities to monitor the implementation of smart specialisations across the EU. Technology areas prioritised by SmartS in partner regions include health, life sciences, ICT, future services, sustainable production technologies and Industry 4.0.
2019

LNG Value Chain for Clean Shipping, Green Ports and Blue Growth in Baltic Sea Region
| Project Budget | 3.300.932,25 Euro |
| Project Duration | 01.05.2016 - 30.04.2019 |
| Lead Partner | Klaipeda Science and Technology Park (LT) |
| Project Partners | Clean Shipping Index (SE); NPPE Klaipeda Shipping Research Centre (LT); Hochschule Wismar, University of Applied Sciences (DE); inwl nonprofit Limited Institute for sustainable Economics and Logistics (DE); World Maritime University (SE); Blekinge Institute of Technology (SE); The Maritime Development Center of Europe (DK); Municipality of Samso (DK); OSK ShipTech A/S (DK); Shipping & Offshore (NO); Baltic Ports Organization (EE); Maritime University of Szczecin (PL); SC Klaipedos nafta (LT); ATI erc gGmbH education, research and furtherance of cooperations (DE); Logistics Initiative Hamburg e.V. (DE); RISE Research Institutes of Sweden (SE); Motus Foundation (PL) |
Wismar University of Applied Sciences participates in the transnational initiative GO LNG: LNG Value Chain for Clean Shipping, Green Ports and Blue Growth in Baltic Sea Region. The project aims to promote clean shipping by increasing the capacity of maritime stakeholders in the Baltic Sea Region (maritime authorities, rescue services, government agencies, shipping companies, ports, research and intergovernmental organisations) to reduce the negative impact of shipping on the marine environment. The project has brought together 19 partners from almost all countries in the Baltic Sea Region to work on realising this ambitious idea. The project is co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF). Wismar University of Applied Sciences is responsible for providing the integrated LNG value chain for BSR (WP3 Leader).
2018
Project name
Green Logistics
| Project Budget | 741.163,00 Euro |
| Project Duration | 15.10.2015 - 14.10.2018 |
| Lead Partner | Hochschule Wismar, University of Applied Sciences |
| Project Partners | Technologische Universität Tallinn (Estland) Linköping Universität (Schweden) Staatliche Bajtursynov-Universität Kostanay, Staatliches Industrieinstitut Rudnyi, Ministerium für Bildung und Wissenschaft, Öffentliche Kaspische Universität (Kasachstan) Nationale Technische Forschungsuniversität Kazan, Staatliche Wirtschaftsuniversität Rostov, Staatliche Polytechnische Universität St. Petersburg und Industrieunternehmen „Betar Ltd.“ (Russland) |
Referring to the results of the EU research project "East-West Transport Corridor II", the European transport sector, especially the Eastern European and Baltic Sea regions, is highly dependent on the development of logistics competences and capacities in Kazakhstan and Russia. Despite the establishment of the monetary union between Russia and Kazakhstan (in 2010) and a high prioritisation of logistics management in the Russian and Kazakh national development strategies, the current level of competences and the reality of the content of studies and the competences taught do not correspond to the actual demand from the EU trading partners.
There is an increasing uneven development in Kazakhstan and Russia - high investments in physical infrastructure (road, rail and transport network) instead of support for the education sector in logistics. The reason for this trend is not a lack of financial basis or political will in Kazakhstan and Russia, but much more a lack of logistics professionals and deficits in the field of logistics skills training. This, in turn, prevents the countries of Kazakhstan and Russia from efficiently implementing their strategic transport policies and discourages European partners and entrepreneurs from investing in the transport sector, which cannot lead to sustainable transport growth.
Taking into account these challenges and aiming to meet the demand for logistics competences, the project will develop and implement the Master's programme "Management of Green Logistics: Strengthening Trans-Eurasian Logistic Accessibility and Connectivity through the Sustainable Logistics Management and ICT Competence Development" together with the partners from Sweden, Estonia and Germany for the partner countries Kazakhstan and Russia. This Master's programme with the acronym "Management of Green Logistics" should be realised in the six partner universities of Kazakhstan and Russia by September 2017.
The project aims to strengthen Trans-Eurasian logistic accessibility and connectivity through sustainable logistics management and ICT competence building, as well as to build the sustainability of logistics competences in the field of intelligent and sustainable transport in the partner universities, thus also strengthening their presence at the international educational level in compliance with the principles of the so-called Bologna Process. Furthermore, interregional cooperation is supported, especially with regard to the fact that today's transport challenges know no borders and are mostly of a global nature. For this reason, a common approach in this field is essential. By introducing complex contents into the respective curricula and a joint implementation of the Master's programme in the partner countries with the support of colleagues from Germany, Sweden and Estonia, the European educational standards are communicated to the partner countries.
Further projects

LogOn Baltic - Developing Regions through Spatial Planning and Logistics & ICT Competence in the BSR.
EPC - Project Partner. 30 Partners from BSR. Read more

InterBaltic - Improving Intermodality and Interoperability in the Baltic Sea Region
EPC - Project Partner. 43 Partners from BSR. Read more

SIIM - Strategic International Management for SME
EPC - Lead Partner. 6 partners from: Finland, Germany and Kazakhstan. Read more

Virtual Campus for SME - ERASMUS-Project.
EPC - Project Partner. 6 partners from: Hungary, France, Germany and UK.
Innovation Network: Logistics Region Wismar - National Research Programme
Networking & Cluster building in maritime logistics

A.S.A.P. Efficient Administrative Structures As a Prerequisite
EPC - Project Partner. 38 Partners from BSR, ca 3,7 Mio EUR.

BBDN - Baltic Business Development Network
EPC - Project Partner. 17 Partners from BSR, ca 3,5 Mio EUR.

International comparative studies and course development on SMEs
EPC - Project Partner. 38 partners from: Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Russia and Sweden
BALTIC BIRD - Improved accessibility of the Baltic Sea Region by air transport.
EPC - Project Partner. 21 Partners, ca. 3,0 Mio EUR Budget. Read more
Baltic.AirCargo.Net - Improvement of the air cargo transport sector by service oriented ICT-methods and processing logistic network
EPC - Lead Partner. 17 Partners from BSR and UK, ca. 3,0 Mio EUR budget. Read more
Design EntrepreneurSHIP - Integration of Students, Graduates and SME’s in terms of Industrial Design Management.
EPC - Project Partner. 4 Partners, ca. 1 Mio EUR Budget. Read more & Project website
MarTech LNG - Marine Competence, Technology and Knowledge Transfer for LNG (Liquid Natural Gas) in the South Baltic Sea Region.
EPC - Project Partner. 8 Partners, ca. 1,4 Mio EUR Budget. Read more & Project website
Green Engine - Environmental Process and Energy Engineering based on Renewable Resources and Bio-Waste
EPC - Lead Partner. 10 Partners from DE, EE, LV, Russia & Kazakhstan, ca. 0,9 Mio EUR Budget. Read more
Transport Cluster – for sustainable, multimodal & green transport corridors in the Baltic Sea Region.
EPC - Project Partner. 8 Cluster Partners from BSR. Read more & Project website
Transport Oversize Baltic - Development of a South Baltic Transport Oversize Strategy
EPC - Project Partner. 9 Project Partners from BSR. Read more & Project website
East West Transport Corridor - development of a "Green Corridor Concept" as a best practice case in the European context.
EPC - Project Partner. 40 Project Partners from BSR, ca. 7,5 Mio EUR Budget. Read more & Project website
E-government as a tool to improve the quality of services provided by public authorities for SMEs in the Baltic Sea region.
EPC - Project Partner. 22 Project Partners from BSR, ca. 2,5 Mio EUR Budget. Read more & Project website